Rock Crystal (Quartz): Rock Crystal is the purest water-clear and colorless from of Quartz. It is known as mountain crystal (Bergkristall). It is the presence of impurities that gives other varieties of quartz their colors. It is found in beautifully formed crystals, often with complex terminations. These are usully bounded by the faces of six-sided prisms, which are almost always striated horizontally. Very often they (read full)
Mountain Green Gemstones & Minerals
The following is a list of Mountain Green gems and minerals listed in our database. Click the pictures to get full data, click the X to remove the gem from the list.
Rutile: Rutile with anatase and brookite is a trimorph of titanium oxide in the Rutile group.
It forms characteristic slender prismatic striated lengthways, variably terminated and often geniculate twinned crystals of the tetragonal system. Elbow- and heart-shaped (geniculated) twin crystals are common.
It is hard, heavy, fragile, with perfect cleavage.
It has a metallic to adamantine lustre an (read full)
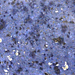
Lazulite: Lazulite is a compact, pleochroitic mineral which forms a series to scorzalite. It is dichroic, with a monoclinic crystal system. It appears as pointed, pseudo-dipyramidal, bright blue crystals in microgranular masses. It is hard, medium heavy, fragile with indistinct prismatic cleavage. It is translucent, with vitreous luster. It is infusible, discolors and breaks into small fragments when heat (read full)
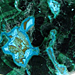
Malachite: Malachite is a bright green, basic copper carbonate. It appears as fibrous, radiating aggregates with silky to dull luster, and its crystals are adamantine. Acicular crystals are common. It commonly occurs as a green film on other copper minerals and as botryoidal or reniform masses with concretionary, banded structure and emerald green color. The color of the glassy, lustrous crystals is dark (read full)
Spodumene: Spodumene is a lithium aluminum silicate that crystallizes in the monoclinic system. It is one of several rock-forming minerals in the Pyroxene group, which are physically-related as their chemical content is quite similar and forms a chain. Fellow pyroxenes are jadeite, enstatite, diopside, hypersthene, augite, acmite, hedenbergite, pigeonite, and aegirineaugite. It appears as prismatic crystals (read full)
Serpentine: Serpentine may refer to a single mineral but more often to a group of minerals including antigorite, chrysotile, clinochrysotile, and lizardite, which are altered products of basic and ultra-basic rocks. Rock composed of these minerals is called serpentinite. It comes in all the hues of green.
In mineralogy, serpentine is divided into three polymorphs, crystals with the same chemical substanc (read full)
Sapphire: Sapphire is the blue variety of Corundum. Sapphires can be a very dark blue, to the point of seeming dense and blackish from a distance, sometimes accompanied by a blue to dull green pleochroism, which is only visible from the side in cut stones. They may also be a strong, but not too bright blue, easily recognizable from a distance, this being the real color. Other possibilities are light, usual (read full)
Tektites: Tektites are glass specimens rich in silica that many believed were actually meteorites. But, the locations in which tektites have been found, and their chemistry, led scientists to suggest that they may not in fact have come from outside planet Earth. Another conjecture is that tektites are formed from rocks that melted after being hit by a meteorite. Tektites actually have a composition not unl (read full)
Pyrope: Pyrope is the iron magnesium and aluminum silicate of the pyrope-almandine series in the Pyralspite group of the Garnet family. Its beautiful deep-red gem quality makes it one of the most popular. Pure pyrope is colorless, but its red color, sometimes very bright, is due to small quantities of chrome in the crystal structure. It appears as dodecahedral or trapezohedral crystals, dark red, usually (read full)
Microcline: Microcline is a silicate of potassium and aluminum, and an alkali member of the feldspar group. It is the phase of this compound that is stable at low temperature. The feldspars are major constituents of the rocks on the earth's crust and comprise some of the most important rock-forming minerals. The four feldspars - orthoclase, sanidine, microcline and anorthoclase - comprise a group called the (read full)