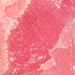
Nephrite: Nephrite is a silicate of calcium, magnesium, and iron, containing fluorine and hydroxyl. It is an amphibole of the actinolite series. It occurs in all colors, also striped and spotted, but the most valuable color is green. The amphiboles of the tremolite-actinolite series usually occur as elongated, parallel, radiating, or even fibrous crystals; but the variety known as nephrite has a very compa (read full)
Calcium Magnesium Iron Silicate Gemstones & Minerals
The following is a list of Calcium Magnesium Iron Silicate gems and minerals listed in our database. Click the pictures to get full data, click the X to remove the gem from the list.
Dravite: Dravite also called Brown Tourmaline is a sodium magnesium-rich mineral in the Tourmaline group of silicates, with a hexagonal system. Other members of this group include elbaite (sodium lithium aluminum rich); schorl and buergerite (sodium iron rich); uvite (calcium magnesium rich); and liddicoatite (calcium lithium aluminum rich). A continuous solid solution series exists between uvite and dravi (read full)
Peridot: Peridot is the greener type of gem-quality specimen of Forsterite-Olivine, which is an important, rock-forming mineral, a silicate of magnesium and iron. Often their names are used interchangeably. The bottle-green/olive green type of olivine is also called olivine. The yellower type of olivine is called Chrysolite. It forms as thick, tabular crystals, frequently with wedge-shaped terminations. T (read full)
Unarovite: Uvarovite is a rare, calcium-chromium emerald-green variety of Garnet. Together with grossular (calcium-aluminum) and andradite (calcium-iron), it makes up the series of ugrandite garnets. These three have similar crystal structure and form, but just have different chemical proportions. It occurs in mixed crystals, so there is a partial replacement of some elements by others. It stands out from t (read full)
Hypersthene: Hypersthene is an important iron-rich orthopyroxene in the Pyroxene group with an orthorhombic crystal system. Other orthopyroxenes forming a complete chemical series with hypersthene are enstatite and bronzite. When the iron content of enstatite increases than it is converted into hypersthene, therefore it is opaque. Pyroxenes are a widespread group of rock-forming silicates. Hypersthene (read full)
Meerschaum: Meerschaum is a clay-like hydrous magnesium silicate. It has no crystals, and occurs as earthy aggregates, porcellanous masses, nodular, and porous. In the fresh state it is soapy and soft, but hard when dried. It sticks to the tongue and its taste sets the teeth on edge. It is opaque, has flat conchoidal, earthy fracture, and an orthorhombic microcrystalline system. Because of its high porosity (read full)
Rhodonite: Rhodonite is a silicate of manganese-iron-magnesium, a mineral of the Pyroxene group, with a triclinic crystal system. It appears as rare tabular crystals, sometimes with rounded edges and wrinkled faces. It sometimes occurs as distinct, translucent to semiopaque crystals, but more often it is in compact, granular, ot crystalline masses of a patchy, pink, flesh red or brownish red color, often wi (read full)
Sinhalite: Sinhalite is a magnesium aluminum borate, and is most commonly found as transparent honey-yellow to brown grains or pebbles with an orthorhombic crystal system. It also appears as pale yellowish, yellow, brown, greenish-brown to black. It occurs in contact metamorphic rocks that are rich in boron, among gneiss or granite where limestones are being replaced through contact with magmatic rock. But (read full)
Vesuvianite: Vesuvianite is a hydrous calcium magnesium aluminum silicate with a tetragonal crystal system. It is the preferred name used by mineralogists for all transparent varieties of Idocrase, the name used by gemmologists. It is a gem mineral that appears in diverse colors, and thus is prized by collectors. A compact green variety of vesuvianite that looks like jade is known as californite. A greenish-b (read full)
Diopside: Diopside is a type of Clinopyroxene, which are abundant, rock-forming minerals. These are embedded and surface-growing crystals, short columnar, and tabular, almost square or octagonal in cross section. It is the magnesium-bearing end member in the isomorphous, monoclinic diopside-hedenbergite series, a complete solid solution series in which two intermediate members, salite and ferrosalite, have (read full)
Kornerupine: Kornerupine is a rare magnesium aluminum borate silicate which occurs as transparent prismatic crystals of the orthorhombic system. It is hard and a has good cleavage in one direction. Colours include a characteristic dark green leaning to brown and a rare and attractive bright vanadium green. This pleochroic colours are brown to greenish brown. Chatoyant stones show a bright eye against a dark g (read full)
Enstatite: Enstatite is the most common silicate under the Orthopyroxene group in the larger classification of Pyroxene minerals (which are rock-forming silicates). Orthopyroxenes form a chemical series composed of the magnesium-rich enstatite, and the iron-containing bronzite and hypersthene. It has an orthorhombic crystal system and appears rarely as stubby, prismatic crystals, but more commonly in fibr (read full)
Pyrope: Pyrope is the iron magnesium and aluminum silicate of the pyrope-almandine series in the Pyralspite group of the Garnet family. Its beautiful deep-red gem quality makes it one of the most popular. Pure pyrope is colorless, but its red color, sometimes very bright, is due to small quantities of chrome in the crystal structure. It appears as dodecahedral or trapezohedral crystals, dark red, usually (read full)
Staurolite: Staurolite is a hydrous magnesium aluminum silicate that crystallizes in the monoclinic system. It appears as coarse, dark gold-brown prisms, or sometimes reddish-brown to black stubby crystals. On weathered rock, it stands out in contrast like sand-coated yellowish brown prisms. Surfaces are often rough or covered with an earthy coating because of natural alteration. It frequently occurs in ch (read full)
Rubellite Tourmaline: Rubellite is the pink to red variety of Tourmaline, which is a complex borosilicate of aluminum and alkali, with iron, magnesium, and other cations. It is found as fine acicular crystals in rocks, or as large individual crystals grown upon matrix where they may reach a weight of several kilograms. Most form elongated and striated trigonal (three-sided) prisms and these are terminated with trigona (read full)
Spinel: Spinel is an extensive group of minerals in which magnesium may be replaced with iron, zinc, and above all, manganese. The hardness and fine colors of gem quality spinel, known as Noble Spinel, set it apart as a gem material from other types of spinel. It normally occurs as distinct octahedral crystals, as clusters also of octahedral habit, or as characteristic twins. The crystals are often iso (read full)
Dolomite: Dolomite is similar to calcite and sits along side it in limestone. It usually occurs as a secondary mineral, formed by the reaction of magnesium-bearing fluids seeping through the limestone. It may be colorless, or white to cream and even yellow brown, sometimes pale pink. It has a vitreous luster and is translucent. The faces of dolomite crystals are often curved, sometimes so acutely that th (read full)
Iolite: Iolite is the violet-colored variety of Cordierite (named after French geologist P. Cordier), a silicate of aluminum and magnesium, with an orthorhombic crystal system. Though the name cordierite is used by mineralogists, the name iolite has become established among gemologists. It appears as stubby, prismatic crystals, pesudo-hexagonal twins with a glassy appearance. It is frequently microgranul (read full)
Taaffeite: Taaffeite is a very rare beryllium magnesium aluminum mineral. No other mineral has both beryllium and magnesium in its composition. It is one of the few gems to be discovered as a faceted stone instead of a rough, as most gemstones are. Rarely cut as a gem, taaffeite looks like a mauve-colored spinel, and its absorption spectrum is similar to it. But gemologists know they've found taaffeite when (read full)
Plasma Chalcedony: Plasma is a massive, semitransparent, leek to dark green variety of Chalcedony (a microcrystalline variety of the Quartz group), microgranular or microfibrous, consisting of speckles of red or brownish-red jasper, resembling drops of blood. It is translucent to opaque, may be dark green to bright-green, apple-green, or nearly emerald-green, containing microfibrous of actinolite, frequently fleck (read full)
Serpentine: Serpentine may refer to a single mineral but more often to a group of minerals including antigorite, chrysotile, clinochrysotile, and lizardite, which are altered products of basic and ultra-basic rocks. Rock composed of these minerals is called serpentinite. It comes in all the hues of green.
In mineralogy, serpentine is divided into three polymorphs, crystals with the same chemical substanc (read full)
Scapolite: Scapolite is a mixed crystal series, a complicated sodium calcium aluminum silicate group composed of calcium-rich meionite, and sodium-rich marialite. It appears as yellow, blue, pink, violet, or colorless prismatic crystals with a tetragonal system, mostly surface-growing, with perfect cleavage. These crystals are usually in aggregates that are massive granular, long columnar, dense, with vitr (read full)
Calcite: Of all minerals, calcite is by far the richest in forms. It appears as rhombohedral, scalenohedral, or prismatic crystals, often intergrown or twinned. It occurs in masses, colorless or in white, pink, green, or yellow, and often visibly thermoluminescent (emits light when heated). Like quartz, calcite often has twinned structure caused by temperature and stress changes. It is semi-hard, wit (read full)
Apatite: Apatite is a gemstone that appears similar to tourmaline in its blue green form. It comes in yellow, green, pink, purple, violet, clear, and cat's eye. The most popular and valuable versions of Apatite are currently the blues that look like tourmaline. In fact its Greek name means "cheat" because it's often passed for other more valuable gems. Apatite streaks white to white yellow. The light gre (read full)
Stichtite: Stichtite is a purplish to pink mineral many times found mixed with green serpentine. Its a hydrated magnesium chromium carbonate hydroxide mineral.With a hardness of 1.5 to 2 on the Mohs scale, stichtite is very soft and used mainly in carvings and ornamental pieces like necklaces or rings. Due to its softness rings and necklaces combine silver or tin to hold the smoothed down pieces in place. (read full)
Hauyne: Hauyne is a blue feldspathoid rock-forming mineral, one of four members of the sodalite mineral group that is a component of lapis lazuli. The other three are lazurite, sodalite, and nosean. It is a complex mineral of sodium, calcium, aluminum silicate, and sulfate. Hauyne forms very bright and attractive though uncommon transparent blue dodecahedral or pseudo-octahedral crystals of the cubic sy (read full)
Sodalite: Sodalite is a sodium aluminum silicate chloride in the Sodalite group with an isometric crystal system. Its royal blue forms are the best known. As a mineral, it is a principal component of lapis lazuli. It appears very rare as dodecahedrons, crystals with 12 faces, but usually it shows as compact masses, bright blue, white or gray with green tints. It is unsaturated and rarely appears with inclu (read full)
Hessonite: Hessonite is the brown-orange variety of Grossular, a nesosilicate in the Garnet group, with an isometric crystal system. It appears with dodecahedral or trapezohedral crystals, cinnamon-brown to orange because of its iron content. Its color matches that of the oil of cinnamon. It also appears as golden-yellow, yellow-brown, or reddish-brown. It is very hard, heavy, fragile, has no cleavage. It (read full)
Euclase: Euclase is a silicate with a monoclinic crystal system. It is considered a very rare gem of light blue color. It appears as long or short prismatic crystals, flattened and transparent. It is colorless, white, green, or blue, commonly a pale aquamarine or green, but crystals of a very fine dark blue (from iron) have been found at the Miami mine in Zimbabwe. Crystals are often striated. It (read full)
Coral: Corals are the supporting framework of small polyps. Each coral polyp, a tiny marine animal that lives in enormous colonies, extracts calcium carbonate from the sea and exudes it through their bases to build a protective home around and above itself. Each generation of polyps dies in its protective home and each succeeding generation builds on top of its predecessor. They precipitate calcareous m (read full)
Epidote: Epidote is widespread, forms a continuous series of minerals, ending with clinozoisite, which contains no iron. It occurs as crystals elongated and often striated parallel to length, and also as massive, fibrous, or granular habits. Epidote has a yellow-green color, ranges from yellowish-greenish to greenish-black. It has vitreous luster, and is transparent to nearly opaque. It has one perfe (read full)
Hematite: Hematite is considered the most important Iron Ore mineral. Its crystals appear as reasonably thick. They may be tabular, or rhombohedral, and occasionally prismatic or pyramidal. Tabular crystals may form as rosettes, when they are called "iron roses." It also occurs as massive, compact, columnar, fibrous, reniform, botryoidal, stalactitic, foliated, and granular. When hematite forms in a renif (read full)
Grossular Garnet: Grossular is a nesosilicate in the Garnet group, with an isometric crystal system. Together with uvarovite and andradite, the three are known as the "ugrandite garnets," an isomorphous series of calcium garnet minerals. It appears with dodecahedral or trapezohedral crystals of various colors; normally characterized by a green color, but also may be colorless, pale green or milky when pure, cinnam (read full)
Zoisite: Zoisite is a hydrous calcium aluminum silicate in the Epidote group, with an orthorhombic crystal system, three crystal axes at right angles to each other, all of varying lengths. It appears in elongated, prismatic crystals, with fine parallel lines on the prism faces and usually poorly terminated. It also appears frequently in formless grains, poorly-defined crystals, rodlike aggregates and gran (read full)
Ivory: Ivory is an organic gem material, largely obtained from the tusks of African and Indian (Asiatic) elephants, but also from the teeth and tusks of the hippopotamus, walrus, and other mammals. Like bones, it consists mainly of calcium phosphate in the form of oxyapatite and a small quantity of calcium carbonate, bound together by large amounts of the proteinaceous organic substance dentine, to form (read full)
Citrine: Citrine is an attractive type of quartz, which is the commonest mineral on the earth's surface. But citrine itself is an uncommon macrocrystalline variety. Its yellow color brought about by its iron hydrate content, its reddish yellow from a trace of ferric iron. It forms hexagonal prisms, terminated by pyramidal shapes. Its faces are often striated, and the crystals twinned and distorted, having (read full)
Phosphophyllite: Phosphophyllite is a very rare mineral, a hydrated zinc iron manganese phosphate with a monoclinic crystal system. It appears as long prismatic or thick tabular crystals. It is colorless to deep bluish-green. Polysynthetic twinned crystals are common. It is semi-hard, light, with excellent prismatic cleavage. Translucent to transparent with vitreous luster. It turns gray and loses water when hea (read full)
Pearl: Pearl is one of four main ornamental materials that are classified as "organic" gems, the other three being coral, ivory, and amber. About 92 percent of pearl is calcium carbonate, in the form of aragonite crystals, held together by an organic substance (concholin), which is identical to the horny outer layer of oyster shells, plus a small quantity of water. Mother-of-pearl has a simila (read full)
Scheelite: Scheelite is a mineral in the group of Sulfates, Chromates, Molybdates, Tungstates. It has the same crystal structure and outside appearance as powellite. But scheelite is a calcium-tungstate, while powellite is a calcium-molybdate.
In rocks, scheelite may appear as crystals like two pyramids connected at its bases, or pseudo-octahedral, or having table-like faces, with detectable p (read full)
Lazulite: Lazulite is a compact, pleochroitic mineral which forms a series to scorzalite. It is dichroic, with a monoclinic crystal system. It appears as pointed, pseudo-dipyramidal, bright blue crystals in microgranular masses. It is hard, medium heavy, fragile with indistinct prismatic cleavage. It is translucent, with vitreous luster. It is infusible, discolors and breaks into small fragments when heat (read full)
Benitoite: Benitoite is a rare gemstone / mineral that fluoresces when lit by black lights. It gets its name from San Benito County, California where it was first found. This gem is almost always blue (it was originally thought to be a sapphire) but also has variations in purple, pink, and clear. Gem prices seem to fluctuate but a few hundred dollars per half ct is common. Why so expensive? The quality gem (read full)
Onyx: Onyx is a translucent to semitransparent variety of Agate, which in turn is a variety of Chalcedony or cryptocrystalline quartz that is porous and consists of straight or parallel banded agate of alternating shades of milky white and black, gray and black, black and red, white and red, white and brown. The term onyx has been erroneously applied as a suffix to Brazilian onyx, Mexican onyx, Orient (read full)
Sard: Sard is the uniformly colored red-brown or brownish-yellow variety of Chalcedony, which in turn is a microcrystalline variety of Quartz. There is no strict separation between sard and cornelian/carnelian (red to reddish brown), because they are both chalcedonies found in the same deposits and were employed for the same objects. The tints of a sard stone may be reddish or orange. Good-quality mat (read full)
Rhodochrosite: Rhodocrosite is a manganese carbonate, a mineral of the calcite series with a hexagonal crystal system. It is isomorphous with calcite and siderite. It occurs as semitransparent, rhombohedral crystals with poor luster, frequently saddle-shaped, growing into druses, or as concretionary masses, sometimes with irregular, contorted veining. It has low hardness and perfect rhombohedral cleavage. Norm (read full)
Aragonite: Aragonite is made from calcium carbonate and found near sedimentary rocks. Colors include clear (when free from impurities), yellow, blue, and even pink. Aragonite can be found in Turkey, France, United States,the bahamas and many other places around the world. Aragonite sand isn't necessarily mined but rather gathered from locations in and around reef systems. This sand is then stored and pack (read full)
Phenakite: Phenakite is a rare beryllium silicate with a hexagonal crystal system. It an attractive hard mineral that resembles quartz. It appears as white or colorless rhombohedral crystals or stubby prisms terminated by multiple rhombohedral faces. Twinned crystals are also common. It may be colorless, yellow, pink, or brown. There are occasional chatoyant specimens, and four-rayed star stones with a brow (read full)
Petalite: Petalite is a lithium aluminum silicate that is an important ore of lithium. This mineral forms, rarely, as small crystals, which are commonly twinned. More often, petalite forms as large, cleavable masses. It may be white, grey, pinkish, yellow, or colorless. It is transparent to translucent, with a vitreous to pearly luster, and fuses with difficulty. It forms in very coarse-grained, acid igne (read full)
Chrysocolla: Chrysocolla is a silicate that forms as stalactitic masses, in radiating groups, or closely-packed aggregates. It appears as green, blue, and blue-green, but can also be brown or black when impurities are present. It may be translucent to nearly opaque, and has a vitreous to earthy lustre. It forms in the oxidation zone of copper deposits, and occurs with azurite, malachite, and cuprite. When d (read full)
Labradorite: Labradorite is a sodium-rich plagioclase feldspar which displays a particular type of iridescence on a dark ground. Plagioclase feldspars are rock-forming, calcium-sodium minerals which form a continuous series ranging from albite, through oligoclase, andesine, labradorite, and bytownite to anorthite. Precise classification is generally not possible in hand specimens, and their physical properties (read full)
Fire Agate: Fire Agate is a term applied to much of the variety of chalcedony that occurs as botryoidal, consisting of crystals of minute platy inclusion of an iron mineral goethite or limonite minerals over the layers of chalcedony, producing a vivid rainbow containing every color in the spectrum, an iridescent, fire-like appearance, with careful polishing away of the brown outside layers. When polished, it (read full)
Pyrite: Pyrite is an iron sulphide mineral with a cubic crystal system and is dimorphous with marcasite. It occurs as cubic crystals with striated faces, or in the form of pentagonal dodecahedra, usually well-crystallized, either isolated or in small, often well-formed groups, or as "iron cross" twins. It is a characteristic, brassy-yellow or pale-gold color, opaque and with a metal luster. It sometimes (read full)
Jadeite: Jadeite is a silicate of sodium and aluminum, and is a member of the Clinopyroxene group of minerals. It is so called because it is the source of one of the ornamental materials commonly known as Jade. It has a monoclinic crystal system, and occurs as granular aggregates of small crystals, but has occasionally been found in crystals of a few centimeters. The color varies a great deal because of t (read full)
Howlite: Howlite an opaque, massive mineral used for ornamental and utilitarian articles. is a rarity for collectors It has a monoclinic tabular crystal system with a subvitreous luster. The most common occurrence is in the form of a cauliflower. Howlite is found in borate deposits, with most ornamental pieces found from various sites in California (USA) and Mexico. It occurs as opaque white, and may be (read full)
Schorl Tourmaline: Schorl is the black, opaque, sodium iron rich variety of Tourmaline, a complex borosilicate with a trigonal crystal system.
Tourmalines usually occur as long, three-sided prisms, which often have well-terminated ends. Sometimes they are found as parallel or radiating groups of long, thin prisms with striated ridges lining its surface. Its varieties span the widest color ranges in the mineral (read full)
Orthoclase: Orthoclase mineral is a silicate of potassium and aluminum, belonging to the Feldspar group. It has the same composition as microcline, but is stable at slightly higher temperatures. It occurs as prismatic, sometimes flat-sided crystals, but in rocks it is usually anhedral. It may be perfectly transparent and yellow or almost colorless, but it is more often semi-opaque and white to grayish-white, (read full)
Obsidian: Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock, a volcanic glass formed by rapid cooling. Its essential component is glass. Its accessory components are magnetite, ilmenite, oxides and other minerals, such as feldspar. It has the same composition as dacite or rhyolite, with less than 1 percent water. Its color is shiny black, with clear conchoidal (shell-like)fracture, its texture glassy with rare micr (read full)
Kyanite: Kyanite is an aluminum silicate that occurs as elongated and tabular in groups of light-blue crystals darker toward the center, or flat, bladed crystals in schists and gneisses, or as radiating rosettes in quartz. It is trimorphous with sillimanite and andalusite. Kyanite is also known as disthene, meaning, "double strength." This refers to the fact that the hardness along the length of kyanite c (read full)
Danburite: Danburite is a silicate of clear, prismatic crystals, with wedge-shaped terminations. It is occasionally pale yellow, a variety of gemstone feldspars group that resembles topaz. It is very hard, heavy, and has a transparent to vitreous to greasy luster. It fuses easily into a colorless glass, coloring the flame green, has a luminescence that is sky blue to pale blue-green, and also shows red therm (read full)
Titanite: Titanite is a very rare calcium titanium silicate that is an important ore of titanium. It is also called Sphene. Its crystals are very rare, brilliant, and sparkles like diamond. It appears as crystals that are prisms with pyramid tips, or stubby, wedge-shaped, flattened crystals, or tabular and platy. There are also titanite crystal twins that have grown side by side or interpenetrated, or in g (read full)
Jasper Chalcedony: Jasper is the opaque form of Chalcedony, the microcrystalline varieties of quartz that form concretionary deposits, partially of organic origin in the case of jasper. It is commonly microscopically fibrous, massive, and has a nearly wax-like luster. It has a lower density than ordinary quartz. It is the archetypal collectable beach pebble, dense, fine crystalline, translucent to opaque, and cons (read full)
Rose Quartz: Rose quartz is a usually cloudy, translucent, delicate pale pink, deep pink, rose-red to quasi-white and often veined variety of Quartz. Also known as pink quartz , rose quartz may occur more often as anhedral masses or rarely as crystals which often reach quite large sizes. Rose quartz almost always occurs in pegmatites in massive crystalline bodies which do not show crystal faces. These larg (read full)
Shell: Shell is the hard, protective, outer layer covering of certain creatures found in saltwater or freshwater, such as mollusks, snails, and turtles. This layer consists of calcium-carbonate and chitin, secreted by the soft tissue mantle of most mollusks. The inner surface of the shell is made from smooth nacre which covers the mantle.
Shell is used as inexpensive material for various purposes (read full)
Sphalerite: Sphalerite is a zinc iron sulfide mineral formed in an isometric system. It is trimorphous with wurtzite and matraite. All three have the same chemical compound but crystallize in three different forms. The most common crystal forms of sphalerite are in dodecahedrons and tetrahedrons, elegant three-sided formations, often twinned, and otherwise usually massive, thus looking like brownish-black or (read full)
Morganite: Morganite is a pale red-purple, rose, salmon to purplish red, slightly pink, cesium-bearing variety of Beryl. The Beryl group of silicates includes the important gem varieties emerald, blue aquamarine, pink morganite, and red and yellow beryl. The color of morganite is usually a soft pink without any overtones. It has glassy luster, like other beryls, but its pleochroism is not noticeable. The p (read full)
Andalusite: The gem Andalusite is a gemstone composed of Lead Sulphate giving it a yellowish hew with a light tint of a rusty red color. Its named after the city Andalusia in Spain where it was first found. Colors generally vary from yellow, to yellow green, to green, to brownish red (more iron in the read hued versions), to purple, and even black. This gem is pleochroic meaning it changes color depending on (read full)
Sillimanite: Sillimanite is a grayish-blue aluminum silicate with an orthorhombic crystal system. It is trimorphic with andalusite and kyanite. All three have the same chemical compound but their atoms each arrange to create three different crystal forms. It appears as long, slender crystals without distinct terminations, in off-white, gray, brown, pale green, slate-blue, blue-green, and these crystals are of (read full)
Ruby: Ruby is the most valuable variety of Corundum. The color varies from fiery vermilion to violet red, but because rubies are pleochroic, different colors are also found in the same stone; bright or sometimes brick red in one direction, tending to carmine in the other. The color is also accompanied by marked fluorescence which is stimulated by ordinary, artificial light, and above all, by the ultra (read full)
Tugtupite: Tugtupite is a mineral closely related to sodalite and hackmanite, all cyclosilicates whose structural silicate tetrahedrons are arranged in rings. It is also called beryllosodalite and reindeer stone, and crystallizes in the tetragonal system. It is found in fine-grained aggregates of crystals with its own distinctive cyclamen colour. Crystals are very small, tetragonal, almost cubic, or as shor (read full)
Platinum: Platinum is a rare and precious metal that occurs as a Native Element, one of the rarest in the Earth's crust. It resembles silver, but it is less reactive and does not tarnish in air, and is thus considered a noble metal. Its greater hardness, higher density, and high melting point also distinguish it from silver. Like gold, another noble metal, the only common acid combination to dissolve it i (read full)
Carnelian: Carnelian is a variety of chalcedony, which is translucent and is red to reddish-brown. It may also occur as flesh-colored chalcedony, known as cornelian or carnelian. It is slightly similar in appearance to its relation, the dark brown chalcedony, sard. The colour of cornelian is caused by colloidally dispersed hematite. Other reddish chalcedonies may have been colored by heating since if they (read full)
Microcline: Microcline is a silicate of potassium and aluminum, and an alkali member of the feldspar group. It is the phase of this compound that is stable at low temperature. The feldspars are major constituents of the rocks on the earth's crust and comprise some of the most important rock-forming minerals. The four feldspars - orthoclase, sanidine, microcline and anorthoclase - comprise a group called the (read full)
Spodumene: Spodumene is a lithium aluminum silicate that crystallizes in the monoclinic system. It is one of several rock-forming minerals in the Pyroxene group, which are physically-related as their chemical content is quite similar and forms a chain. Fellow pyroxenes are jadeite, enstatite, diopside, hypersthene, augite, acmite, hedenbergite, pigeonite, and aegirineaugite. It appears as prismatic crystals (read full)
Oligoclase: Oligoclase is a mineral of the plagioclase feldspar series, other members of which are Labradorite and Anorthite. It forms as tabular crystals, which are commonly twinned, with parallel or criss-cross twinning striations. It appears as massive, granular, or compact. It may show brilliant reflections from inclusions. It is light, transparent to translucent, with a vitreous luster and may come in (read full)
Goshenite Beryl: Goshenite is a colorless sodium-rich gem variety of Beryl, a group which includes Emerald and Aquamarine. Other gem beryls include Heliodor and Morganite. It also appears are pale-green, apple-green, to bluish. All beryls are resistant to chemicals with the exception of fluoric acid. They are brittle and therefore easily damaged by knocks, have a vitreous luster, and occur with aquamarine. Their (read full)
Spessartine: Spessartine is the manganese-aluminum variety of Garnet, belonging to its sub-group of aluminum garnets. Garnets are a group of silicate minerals that all crystallize in the isometric system and have the same chemical formula, but in a diversity of proportions, so garnets show up as different varieties, in a broad range of environments. Spessartine possesses the form typical of garnet crystals, w (read full)
Gypsum: Gypsum is the most common sulphate mineral. It is usually the first evaporite mineral to be precipitated form water due to its poor solubility. Varieties include Selenite (or "spectacle stone), which is colorless and transparent; Satin Spar, the fibrous, translucent form with silky luster, which when cut cabochon shows pearly chatoyant effects; Alabaster, used for ornaments, which is firm, fine-gr (read full)
Fluorite: Fluorite is a widely-distributed mineral in the Halide classification, and is now mined in vast quantities. It is a suitable mineral for collectors and is rarely cut as a gem, but massive varieties are carved as ornamental objects. It appears in cubes, octahedrons, dodecahedrons, while other forms are rarer. Compact, banded, and concretionary masses are frequently found. Most fine crystals of flu (read full)
Tektites: Tektites are glass specimens rich in silica that many believed were actually meteorites. But, the locations in which tektites have been found, and their chemistry, led scientists to suggest that they may not in fact have come from outside planet Earth. Another conjecture is that tektites are formed from rocks that melted after being hit by a meteorite. Tektites actually have a composition not unl (read full)
Heliodor Beryl: Heliodor is a gem variety of Beryl with golden-yellow or light yellow-green color. In many cases heliodor is also used to include gems known as Golden beryl/ Golden emerald, though not to be confused with gold beryl. It is sometimes hard to establish a dividing line between heliodor and golden beryl. Its main characteristic is its color, which is the yellow-green of olive oil. Its pigment is uran (read full)
Datolite: Datolite is a semi rare silicate mineral of the gadolinite group. It appears as surface-growing, short and stubby, prismatic, large crystals. Its crystal structure is monoclinic, as it has two axes of unequal length inclined to each other, with the third lateral axis at a right angle to the plane that contains the other two. Its aggregates are huge, granular, dense, fibrous, and has porcelaneou (read full)
Malachite: Malachite is a bright green, basic copper carbonate. It appears as fibrous, radiating aggregates with silky to dull luster, and its crystals are adamantine. Acicular crystals are common. It commonly occurs as a green film on other copper minerals and as botryoidal or reniform masses with concretionary, banded structure and emerald green color. The color of the glassy, lustrous crystals is dark (read full)
Zircon: Zircon is a zirconium silicate with a tetragonal crystal system, and also contains thorium and uranium. It appears as stubby, prismatic, isolated or sometimes dipyramidal, like two pyramids connected at their bases; or in twins, colorless to yellow, red, brown, gray or green, in irregular granules. It is very hard, heavy, with indistinct cleavage, and shell-like fracture. It is sometimes perfect (read full)
Smithsonite: Smithsonite is a mineral in the group of Nitrates, Carbonates, Borates, with a hexagonal crystal system. It appears uncommonly in rhombohedral or scalenohedral crystals. But most of the time it appears with curved faces, like a thick creamy aqua-green mixture poured on rock and left to aggregate in clusters shaped like bunches of grapes, rounded, kidney-like, or to form like elegant icicles, and (read full)
Moonstone: The variety name Moonstone is usually used to describe an optical effect and unlike most variety names it is not confined to a single species (The term is also applied to albite-moonstone, microcline-moonstone, labradorite-moonstone). But Moonstone most prominently refers to the orthoclase feldspar, Adularia Moonstone, a microperthitic association of orthoclase and albite) and rarely to Albite M (read full)
Topaz: The transparent, colored crystals, which also have good luster, are widely used as gems.
Topaz is a silicate of aluminum containing fluorine and hydroxyl which occurs in a variety of delicate colors, nicely added by impurities.
It is often found in short to long crystal prisms with pyramid-shaped ends, or just clean finished edges. It is often white, semiopaque, milky, or a faded yellow, (read full)