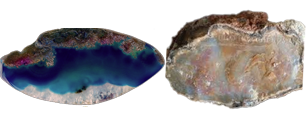
 Photo of Agate Chalcedony in Processed & Rough Form
Photo of Agate Chalcedony in Processed & Rough Form
Agate Chalcedony is a mineral with a hardness of 7 out of 10 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness [?]. These Trigonally structured gems are made of silicon dioxide, their full chemical compound being SiO2.
Agate Chalcedony differs from other Chalcedony in that it often has distinct banding. In fact some slices of Agate may appear to have banding similar to that of tree rings. Due to its porous nature it is often colored (by humans) black, red, green, or blue to further increase its visual appeal.
Agate Chalcedony is found in Brazil, China, Germany ,Hungary, Mexico, Uruguay, the United States, and many other countries around the world.
Slices of this gem are usually very affordable and a staple of amateur and professional collectors alike.
Some but not all Geodes and Geode slices may contain Agate.
What exactly is Agate Chalcedony?
Agate is a variety of chalcedony (microcrystalline quartz) characterized by its distinct banding patterns and colors. It forms in layers within rock cavities.
What causes the different colors in Agate?
Colors come from mineral impurities during formation. Iron creates reds and browns, manganese makes black or pink, chromium produces green, and titanium gives blue hues.
Where is Agate found?
Major deposits exist in Brazil, India, Madagascar, USA (especially Montana and Oregon), Mexico, and Germany. Each location produces agates with distinctive patterns.
How can I tell if my Agate is real?
Real agate has natural banding, is cool to touch, harder than glass (6.5-7 Mohs), and shows no air bubbles. Patterns should be irregular and unique.
Are all Agates naturally colored?
No. While natural agates exist, many commercial agates are dyed to enhance color. Natural agates typically have more subtle, earthy tones.
What are common uses for Agate?
Used in jewelry, decorative items, and cabochons. Historically used for carved seals, tools, and ornamental objects. Industrial uses include grinding stones and burnishing tools.
The specific gravity [?] for Agate Chalcedony is 2.61, its refractive index [?] is 1.53-1.54, and its double refraction [?] is 0.004.









